By Muthiah Kasi, PE, SE, CVS-Life, FSAVE
In the late 60’s, Thomas Snodgrass and Ted Fowler recognized the importance of customer preferences in promoting any product or project. They developed a function logic diagram known as Customer FAST Diagram. Recently SAVE International labelled this diagram as a Customer Function Model. A Customer Function Model is especially effective in the planning or during the conceptual phase of a project.
A Technical FAST diagram logically displays the functions to solve a problem or addresses an issue. It is widely used by Value Engineers and designers to identify critical functions and effectively perform them with the least amount of effort. The Customer Function Model is a classification tool. It classifies the functions from the customer point of view.
The driving force behind each product will be expressed as a task, basic and supporting functions. The task defines the driving force and the basic functions satisfy the task. Every competing product in the market will satisfy the basic function. The difference of any product depends upon how well a specific product performs the four enhancing functions. The enhancing functions are; Assure Dependability, Assure Convenience, Satisfy Stakeholders and Attract Stakeholders.
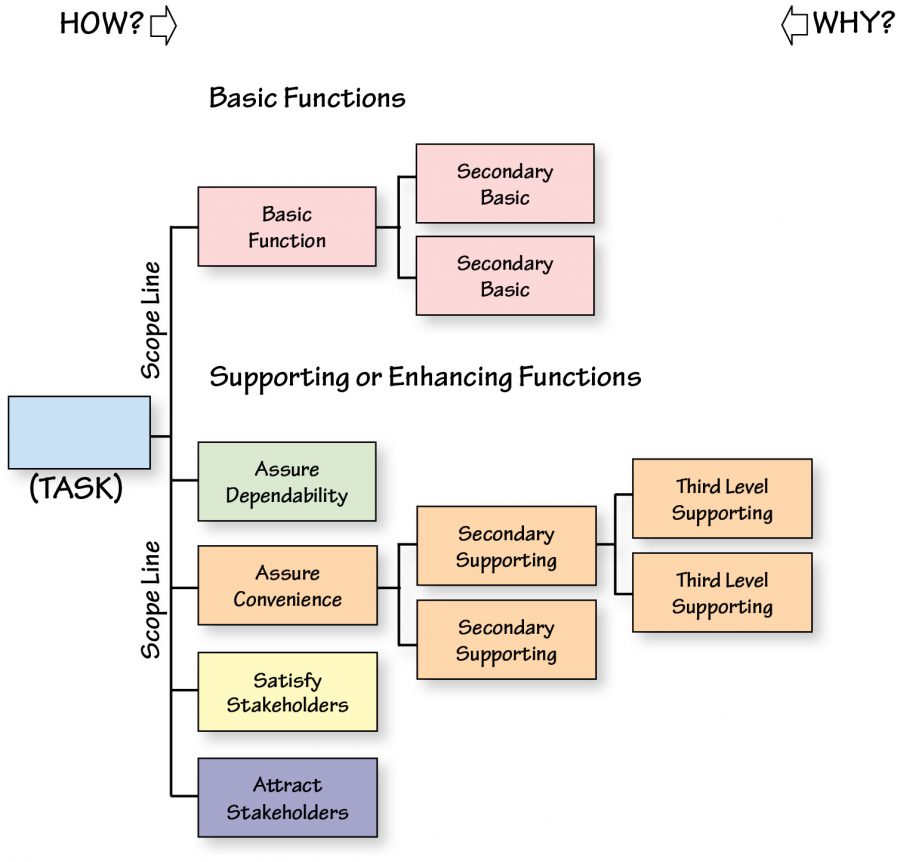
In short, customers always want a stronger and reliable product. Obviously it should be safer, last longer and should be convenient to use. Exhibit A shows the Customer Function Model and its components. Customers and clients are generally referred herein as stakeholders. Stakeholders include users, owners and other interested individuals.
Function Classification
Task
The first step is to determine the task of any product or project. The task satisfies the overall purpose of the product or project. Establish a scope line just to the right of the task. Functions that answer the question “Why perform the task?” lie outside the scope. The concept of establishing the scope line is similar to the one discussed under Technical Function Logic Diagram.
Basic Functions
The second step is to separate the identified functions into basic and supporting functions. Basic functions are those which are essential to the performance of the task. Without the basic functions, the project or process will not work.
Supporting or Enhancing Functions
The third step is to group the remaining functions into the four primary supporting functions. For example, consider the role basic and supporting functions play in a building. Structural engineers concentrate primarily on the basic functions, with heavy emphasis on the supporting function Assure Dependability. Mechanical engineers and electrical engineers pay more attention to the supporting function Assure Convenience, while architects satisfy the basic and supporting functions Satisfy Stakeholders and Attract Stakeholders. The four categories of supporting or enhancing functions are defined as:
Assure Dependability—function(s) that have at least one of the following attributes:
- Makes the elements of the project/product stronger or more reliable or effective
- Makes it safer to use
- Lengthens the life of the parts or minimizes maintenance
Assure Convenience—function(s) that have at least one of the following attributes:
- Modifies the basic function to make it convenient to use
- Enhances spatial arrangements
- Facilitates maintenance and repairs
- Furnishes instructions and directions to stakeholders
Satisfy Stakeholders —function(s) that have at least one of the following attributes:
- Modifies the basic function to satisfy individual desires
- Protects the environment
- Makes the stakeholder’s life more pleasant. (Minimize Noise would be an example.)
- Makes the element appear to be better in the opinion of the stakeholder, but not necessarily in the opinion of the designer. Function added at the request/requirement of the stakeholder that is not otherwise required to implement the project or product.
Attract Stakeholders—function(s) that have at least one of the following attributes:
- Emphasizes the visual aspect or other senses
- Projects a favorable image (aesthetic attributes)
How to Classify Functions?
Function classification depends upon stakeholders, environment and timing. The function Drain Water in a highway or roadway can be classified in any one of the four categories depending upon the environment. For a highway that has a speed limit of 70 MPH undrained water can cause hydroplaning. This can cause major accidents. In such a case Drain Water is a dependability function. If a highway has two or more lanes in each direction and is lower speed, water may encroach one lane. In such a case the drivers will tend to avoid the lane and use the other lanes. This may reduce the capacity of the highway resulting in classifying the function Drain Water as a convenient function. In commercial areas, such as a parking lot, customers will not want to traverse ponded water in the lot. In such a case Drain Water is an attract stakeholder function. In local streets with 25 MPH speed limit, residents do not like to see water ponding in front of the house. In such a case, the function Drain Water is classified as satisfy stakeholder function.
Importance of Function classification
Function classification (and assignment of function costs) helps designers to understand where the costs of a project are going and assist in developing options that meet their needs and desires. On a recent highway VE project, the preliminary design was based on the stakeholder’s design policy that indicated the need for a third lane to accommodate traffic and reduce delays. This expense will be justified if it is in the dependable category of functions. However, what if the traffic that demands the upgrade (based on policy) only occurs on the weekend (recreational traffic)? If the city wants to attract more recreational businesses, the function (and associated costs) would be assigned to an attract stakeholder category. If the recreation traffic is not a driving force of the project (not a dependability function) this function can be moved to the satisfy stakeholder category. This was the case on the VE and the VE Team identified this function’s cost as a mismatch. The client accepted this logic and eliminated the need for a third lane.
Function Measurement
In a typical infrastructure project, the distribution for a Customer Function Model is close to what is shown below:
| Basic Functions | = | 20.00% |
| Assure Dependability Functions | = | 30.00% |
| Assure Convenience Functions | = | 25.00% |
| Satisfy Stakeholders Functions | = | 15.00% |
| Attract Stakeholders Functions | = | 10.00% |
There is no definite ratio for each classification. For example, this distribution for a warehouse building will have higher percentage for basic and dependability functions. For a train station the cost of convenient functions will be higher.
Summary
A Customer Function Model outlines or presents the customer perspective to designers and manufacturers. (Technical) FAST diagramming is the appropriate tool to design a product or project to satisfy the customer/client preference.
